Injection Molding
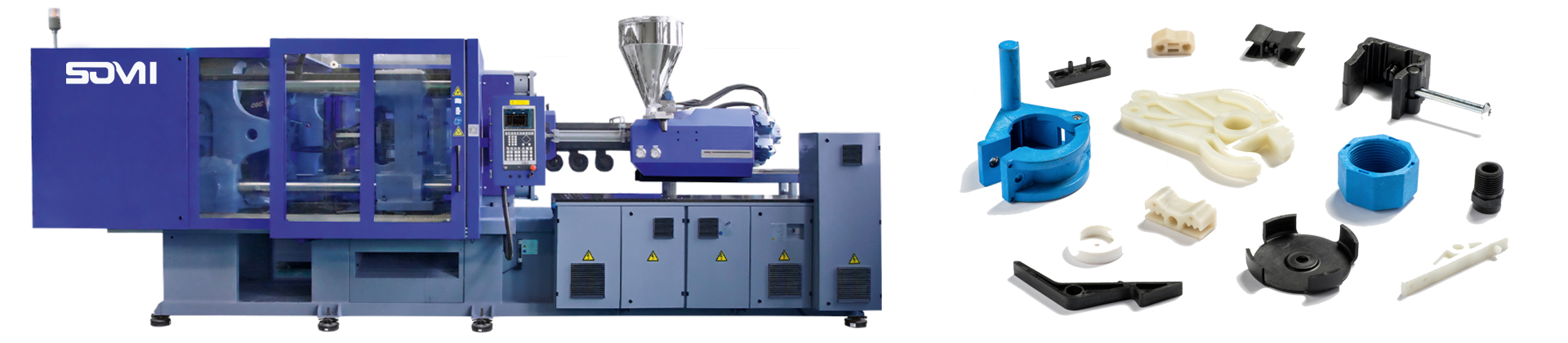

SOMI Capability
SOMI Injection Molding Capability
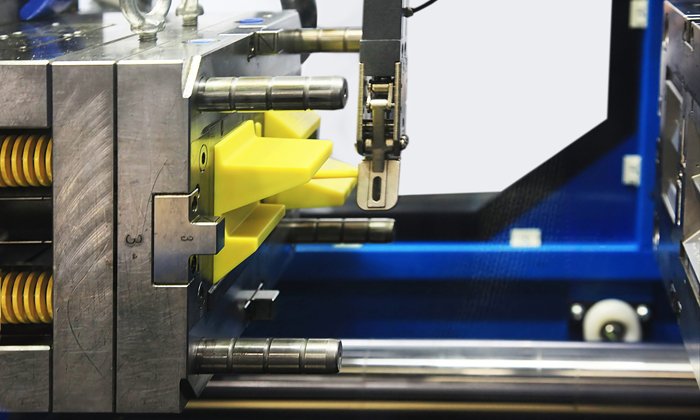
Plastic Injection Molding
Plastic injection molding is a highly efficient and precise manufacturing process that involves injecting molten plastic into molds to create a wide range of complex plastic products.
Low cost, Stable quality.
Short production cycle, Suitable for large-scale production.
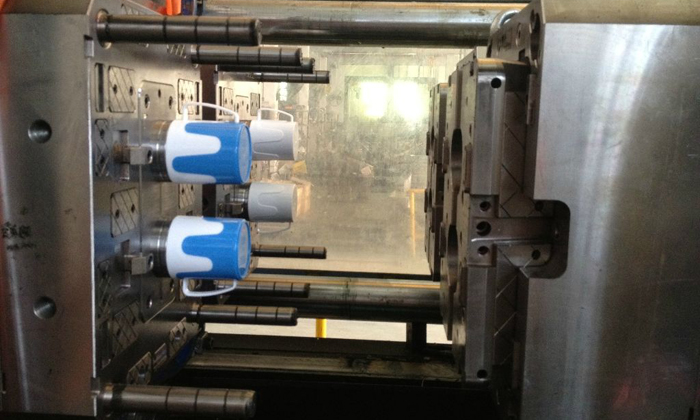

Bi-color Injection Molding
Bi-color injection molding is a specialized process that allows for the production of plastic parts with two different colors or materials in a single operation.
Product appearance diversity, Design flexibility, Cost saving.
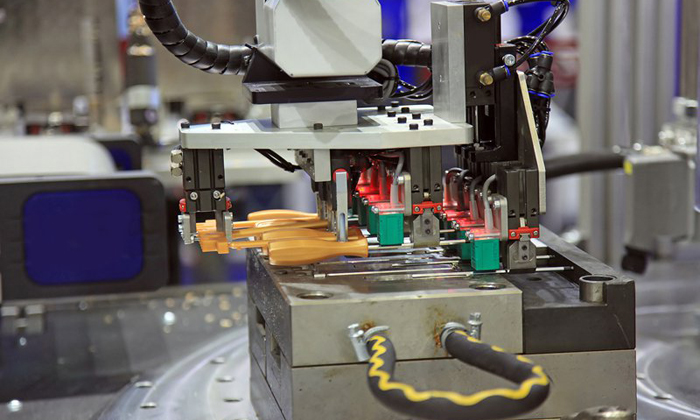
Insert Molding
Insert molding is a specialized injection molding process that involves inserting metal or plastic parts into the mold cavity before the molten material is injected.
Improved part strength and structural integrity.
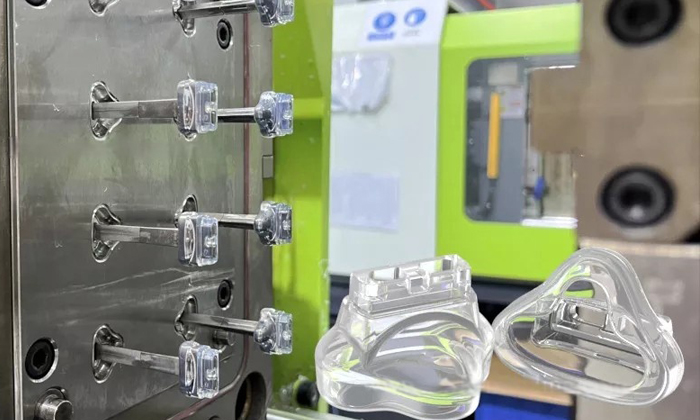

Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding
Liquid Silicone Rubber Molding, also known as LSR molding, is a popular manufacturing process used to create precision silicone rubber parts. This process involves injecting liquid silicone material into a mold cavity, where it is then cured to form the desired product.
Excellent temperature resistance, durability, and chemical stability.
Injection Molding
Show Custom Parts Machined by SOMI
Injection Molding
Injection Molding Materials
 Common Injection Molding Materials
Common Injection Molding Materials
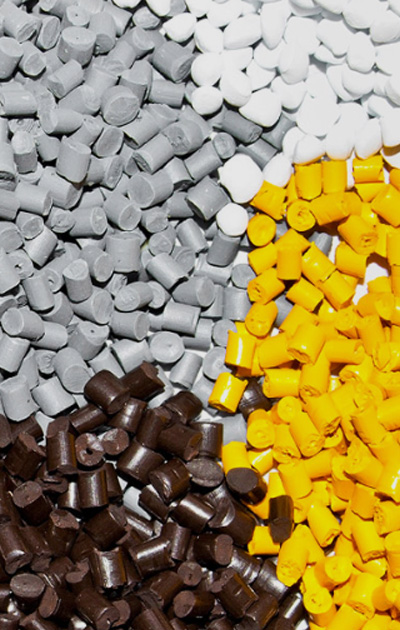


- ABS
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- PVC
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- POM
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- Polypropylene(PP)
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- Nylon
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- PET
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- PTFE(Teflon)
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- FR-4
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- Polycarbonate(PC)
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- PMMA
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- Polyethylene(PE)
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.

- PEEK
It is a thermoplastic polymer material with high strength, good toughness, corrosion resistance, high temperature resistance.
Injection Molding
Injection Molding Surface Finishes

As-machined
The standard finish of our parts, the "machined" finish, has a surface roughness of 3.2 μm (126 μin), which removes sharp edges and cleanly removes burrs from the part.
Machining Texture:There are slight scratches on the visible surface.

Smooth machining
A finishing CNC machining operation can be applied to the part to reduce its surface roughness. The standard smoothing surface roughness is Ra 1.6 μm (64 μin). Light surface scratches are visible.
Machining Texture:Visible, light surface scratches.

Fine machining
Refers to the process of precision treatment of raw materials or semi-finished products. The standard smoothing surface roughness is Ra 0.8 μm (32 μin).
Machining Texture:Slightly visible.

Bead blasting
Bead blasting refers to the use of round spherical media that, when impacted against the surface of a part, will leave a more uniform finish caused by the sphere “dimpling” the surface.
Machining Texture:Frosted grain.

Brushing
Brushing is a surface treatment process that uses abrasive belts to draw traces on the surface of a material, usually for aesthetic purposes.

Polishing
From Ra 0.8 to Ra0.1, the polishing process uses abrasive materials to rub the surface of the part, making the surface of the part more shiny, depending on your requirements.
Machining Texture:Smooth, glossy finish

Anodizing
Aluminum and its alloy in the corresponding electrolyte and specific process conditions, due to the action of external current, the process of forming an oxide film on the aluminum product.
Machining Texture:Smooth, matte finish.

Electroplating
Electroplated coating preserves the surface of parts and resists rusts and other defects from causing decay by applying electric currents to reduce metal cations.
Machining Texture:Smooth, glossy finish.

Electroless nickel plating
Electroless nickel plating is a process that deposits an alloy of nickel-phosphorus onto the surface of a metal. This process is chemical only, so does not involve the use of electricity.
Machining Texture:Reduced but visible.

Black oxide
Black oxide is a conversion coating similar to Alodine that is used for steel and stainless steel. It is used mainly for appearance and for mild corrosion resistance..
Machining Texture:Smooth, matte.

Powder coating
Using corona discharge, we make the powder coating adsorbed to the part, creating a more wear-resistant layer with a typical thickness ranging from 50 μm up to 150 μm.
Machining Texture:Glossy.

Chromate conversion coating
Chromate conversion coating is a type of conversion coating, used on aluminum as a corrosion inhibitor, as a primer for paint due to increased adherence or to preserve electrical conductivity.
Machining Texture:Visible.

Electrophoresis
In the solution under the action of direct current electric field, the charged resin moves to the opposite electrode phenomenon. Strong corrosion resistance, can be on different colors.
Machining Texture:Visible.

As-machined
The standard finish of our parts, the "machined" finish, has a surface roughness of 3.2 μm (126 μin), which removes sharp edges and cleanly removes burrs from the part.
Machining Texture:There are slight scratches on the visible surface.

Smooth machining
A finishing CNC machining operation can be applied to the part to reduce its surface roughness. The standard smoothing surface roughness is Ra 1.6 μm (64 μin). Light surface scratches are visible.
Machining Texture:Visible, light surface scratches.

Fine machining
Refers to the process of precision treatment of raw materials or semi-finished products. The standard smoothing surface roughness is Ra 0.8 μm (32 μin).
Machining Texture:Slightly visible.

Bead blasting
Bead blasting refers to the use of round spherical media that, when impacted against the surface of a part, will leave a more uniform finish caused by the sphere “dimpling” the surface.
Machining Texture:Frosted grain.

Brushing
Brushing is a surface treatment process that uses abrasive belts to draw traces on the surface of a material, usually for aesthetic purposes.

Polishing
From Ra 0.8 to Ra0.1, the polishing process uses abrasive materials to rub the surface of the part, making the surface of the part more shiny, depending on your requirements.
Machining Texture:Smooth, glossy finish

Anodizing
Aluminum and its alloy in the corresponding electrolyte and specific process conditions, due to the action of external current, the process of forming an oxide film on the aluminum product.
Machining Texture:Smooth, matte finish.

Electroplating
Electroplated coating preserves the surface of parts and resists rusts and other defects from causing decay by applying electric currents to reduce metal cations.
Machining Texture:Smooth, glossy finish.

Electroless nickel plating
Electroless nickel plating is a process that deposits an alloy of nickel-phosphorus onto the surface of a metal. This process is chemical only, so does not involve the use of electricity.
Machining Texture:Reduced but visible.

Black oxide
Black oxide is a conversion coating similar to Alodine that is used for steel and stainless steel. It is used mainly for appearance and for mild corrosion resistance..
Machining Texture:Smooth, matte.

Powder coating
Using corona discharge, we make the powder coating adsorbed to the part, creating a more wear-resistant layer with a typical thickness ranging from 50 μm up to 150 μm.
Machining Texture:Glossy.

Chromate conversion coating
Chromate conversion coating is a type of conversion coating, used on aluminum as a corrosion inhibitor, as a primer for paint due to increased adherence or to preserve electrical conductivity.
Machining Texture:Visible.

Electrophoresis
In the solution under the action of direct current electric field, the charged resin moves to the opposite electrode phenomenon. Strong corrosion resistance, can be on different colors.
Machining Texture:Visible.
Industry
Application Areas of Injection Molding
Consumer Electronics
Our manufactured electronic components consistently meet the tight tolerances required in this ever-evolving industry.
Learn More
Aerospace & Aviation
Our manufactured electronic components consistently meet the tight tolerances required in this ever-evolving industry.
Learn More
Automotive
Our manufactured electronic components consistently meet the tight tolerances required in this ever-evolving industry.
Learn More
Medical
Our manufactured electronic components consistently meet the tight tolerances required in this ever-evolving industry.
Learn More
Robotics & Automation
Our manufactured electronic components consistently meet the tight tolerances required in this ever-evolving industry.
Learn More
Industrial Machinery Parts
Our manufactured electronic components consistently meet the tight tolerances required in this ever-evolving industry.
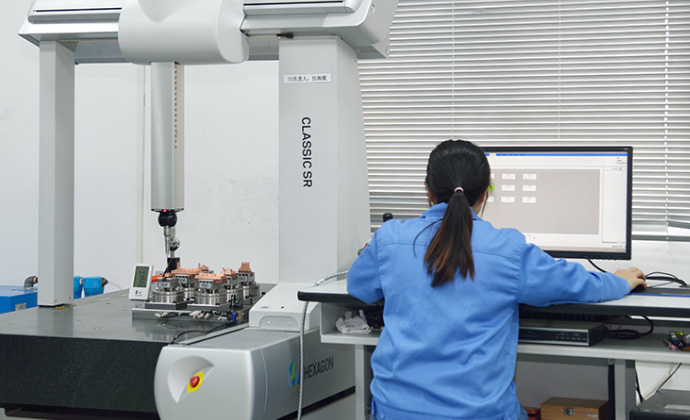
Learn MoreTest Inspection
Quality Assurance at the Heart of Our Operations

Get a Quote
Contact us Today for Your Injection Molding Requirements
Ready to elevate your manufacturing with the precision and quality of SOMI's Injection Molding services? Contact us today to discuss your project and discover how we can help you achieve unparalleled results. With SOMI, you're not just choosing a service provider, you're choosing a partner dedicated to your success.
We hope to discuss potential cooperation opportunities with you and ask you to provide quotation information for your project. Looking forward to your reply and working with you to promote the success of your project!
- *Name
- *Tel
- *Title
- *Content
FAQ
Frequently Asked Questions
- Q: What is injection molding?A: Injection molding is a manufacturing process used to produce parts by injecting molten material into a mold. It is commonly used with plastics but can also accommodate metals, glasses, and elastomers. The process begins with melting the material, which is then injected under pressure into a mold cavity. Once the material cools and solidifies, the mold is opened to eject the finished part. This technique is favored for its ability to produce large volumes of identical parts with high precision, complex shapes, and excellent surface finish. Injection molding is efficient and cost-effective, particularly suitable for mass production.
- Q: What is the difference between plastic injection molding and 3D printing?A: 3D printing is better for small batch, complex parts that may require frequent design changes or customisation. Injection moulding, on the other hand, is better for large volume production of less complex parts that have successfully completed the design stage.
- Q: What is the main advantage of plastic injection compared to additive manufacturing?A: The main advantage of injection molding compared to additive manufacturing is the production of large volumes of identical parts. However, injection molding faces significant challenges, notably in setup time and initial investment.










